Squid Proxy Server
Squid Proxy Server
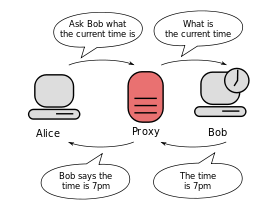
Proxy server
In computer networks, a proxy server is a server (a computer system or an application) that acts as an intermediary for requests from clients seeking resources from other servers. A client connects to the proxy server, requesting some service, such as a file, connection, web page, or other resource available from a different server and the proxy server evaluates the request as a way to simplify and control its complexity. Proxies were invented to add structure and encapsulation to distributed systems.[1]Today, most proxies are web proxies, facilitating access to content on the World Wide Web and providing anonymity.
Squid is a proxy server and web cache daemon. It has a wide variety of uses, from speeding up a web server by caching repeated requests; to caching web, DNS and other computer network lookups for a group of people sharing network resources; to aiding security by filtering traffic. Although primarily used for HTTP and FTP, Squid includes limited support for several other protocolsincluding TLS, SSL, Internet Gopher and HTTPS.
Squid was originally designed to run on Unix-like systems. A Windows port was maintained up to version 2.7, but more current versions are not being developed. Squid is free software released under the GNU General Public License.
Supported operating systems
Squid can run on the following operating systems:
- AIX
- BSDI
- Digital Unix
- FreeBSD
- HP-UX
- IRIX
- Linux
- Mac OS X
- Microsoft Windows
- NetBSD
- NeXTStep
- OpenBSD
- OS/2 and eComStation
- SCO OpenServer
- Solaris
- UnixWare
Content filtering,
URL Restriction,
Privillege Level of Internet Distribution,
Surfing Monitoring,
Reporting,
User,
Password,
Mac,
Active Directory,
MySql,
LDAP Integration,
MIME Protection,
Antivirus,
AntiSpy,
Control Panel,
Log Analysis,
Speedy Internet Connection,